Related product:
PosiTest CMM IS
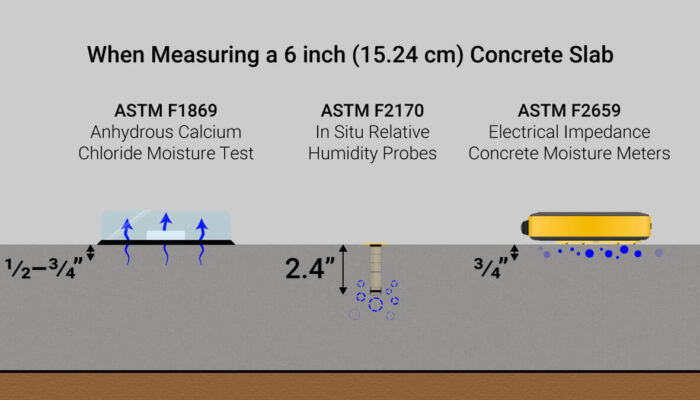
In situ concrete moisture (RH) probes—such as the PosiTector CMM IS—described in ASTM F2170 are designed to determine % RH (relative humidity) within a concrete slab. With the limitation of anhydrous calcium chloride tests and impedance meters only measuring the moisture condition within the top 1 inch of a concrete slab, a full understanding of absolute moisture content has been impossible with those methods.
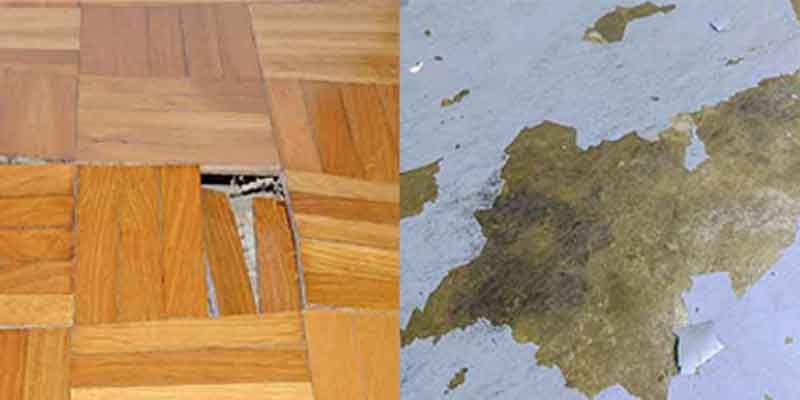
“5.1 Excessive moisture in floor slabs after floor covering has been installed can cause floor covering system failures such as debonding, peaking and deterioration of finish flooring and coatings and microbial growth.
5.2 Manufacturers of such systems generally require moisture testing to be performed before installation on concrete. Internal relative humidity testing is one such method.”
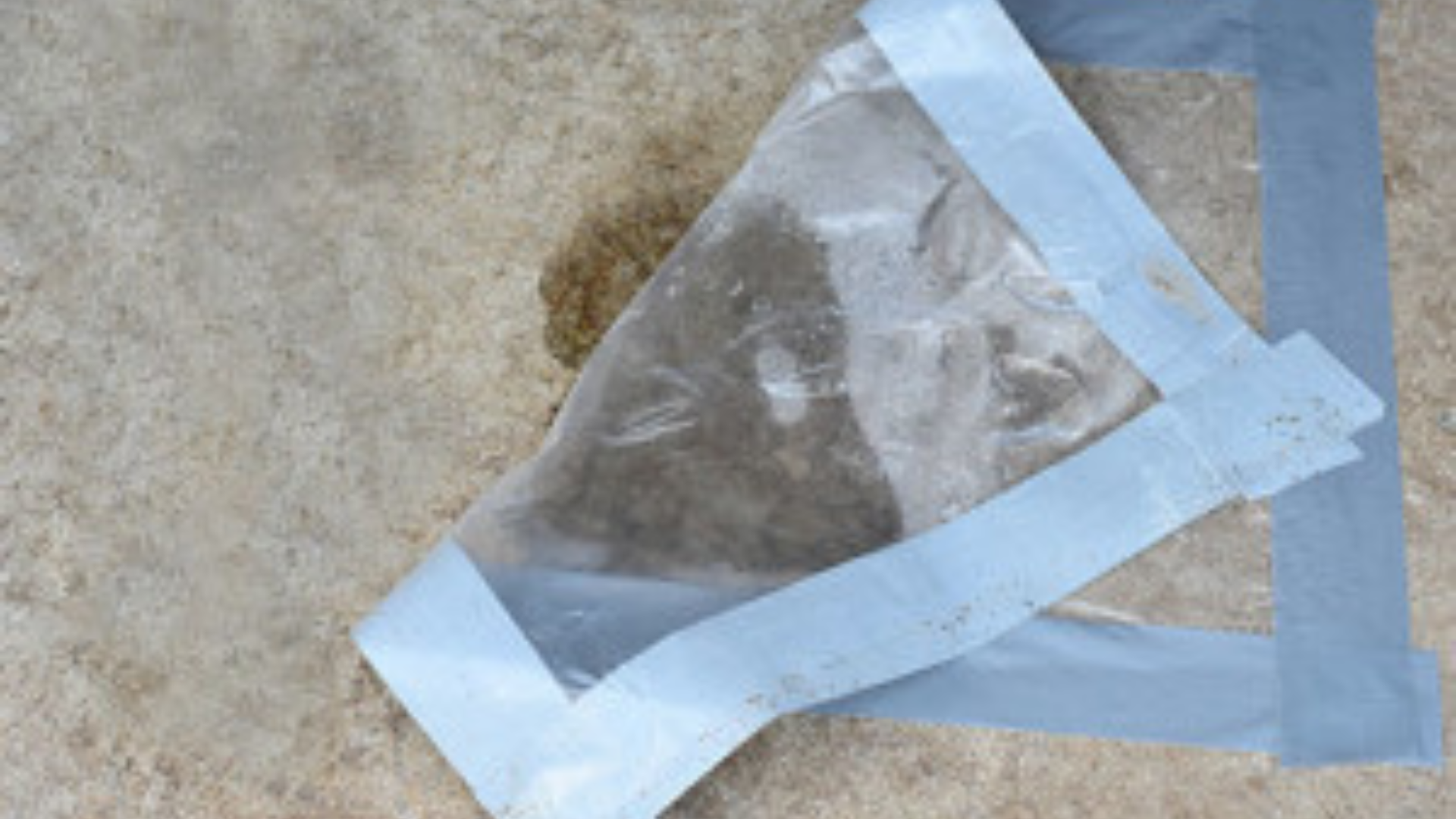
ASTM F2170 addresses these issues and is considered to be the reliable and preferred method for determining the moisture condition within a new concrete slab. By drilling a hole to 40% of maximum slab depth* and placing the probe directly into the slab, an isolated chamber is created allowing for very targeted testing within the slab.

“ASTM F2170 requires 3 probes for the first 1,000 ft2 (100 m2) and another probe for each additional 1,000 ft2 (100 m2). One test must be performed within 3 ft (1 m) of each exterior wall.”* To identify additional locations for the in situ probes, consider using an impedance meter as described in ASTM F2659, such as the PosiTest CMM to detect areas of increased moisture content.†
*Refer to ASTM F2170 for a complete description of the method
†% relative humidity requirements are often specified by flooring manufacturers. It is strongly recommended that the user refer to these to determine proper moisture conditions before installation of a flooring system.
 My Account
My Account